Let’s Collaborate.
Achieve your desired properties: cost, grain structure, purity, or a number of other variables.
RSC is uniquely positioned to serve our customers with products specifically fabricated or processed to their exact specifications, with proprietary quality control methods to certify the product is free from voids, inclusions, and meets purity requirements.
Click below to learn more about the product sub-categories:
Precious Metal Sputtering Targets
Metal Management
RSC manages metal accounts for many of our customers. Precious metal can be bank transferred or purchased into metal accounts, also known as pool accounts. Reclaim material can also be directly deposited into a customer’s metal account. We also offer customer-specific strategies designed to more closely match in timing, the precious metals purchase price to our customer’s end product cost.
Precious metals for physical vapor deposition (PVD) has historically been the realm of juggernaut corporations with customer service and product pricing to match. Experience the difference with a focused, financially strong company built on customer responsiveness.
Tell us what technical and commercial variables for thin film coatings are most important for your company. Whether it be fabrication cost, metal management, grain structure, material purity, something else, or a combination thereof, RSC delivers a sputter target that best meets our customer’s needs, not our convenience.
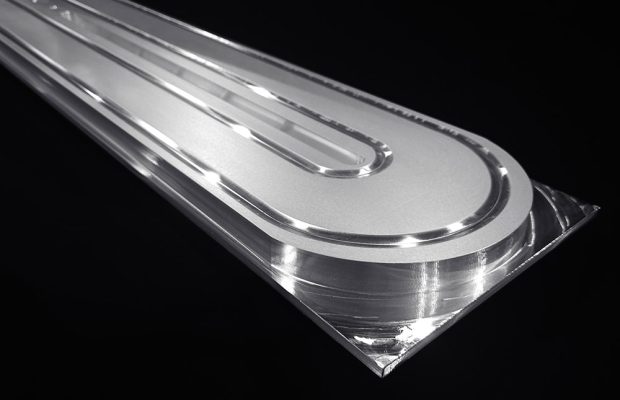
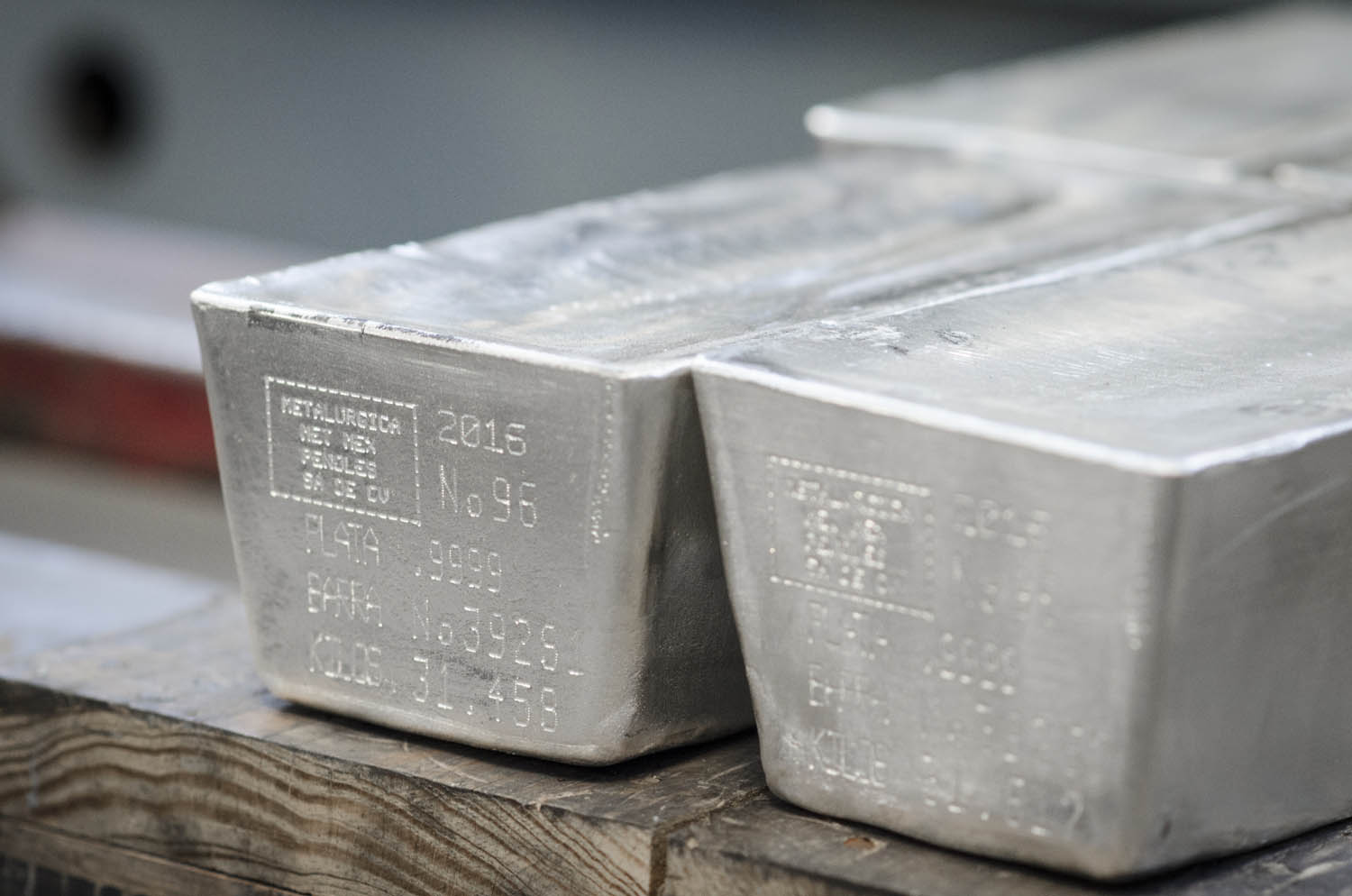
Precious Metal Sputtering Targets
- Gold (Au) Targets – 4N (99.99%) and 5N (99.999%)
- Silver (Ag) Targets – 4N (99.99%) and 5N (99.999%)
- Platinum (Pt) Targets – 4N (99.99%)
- Palladium (Pd) Targets – 3N5 (99.95%), higher purity available on request
- Precious Metal Alloy Targets – Please inquire about our alloy targets
Specialty Metal Sputtering Targets
- Nickel (Ni) Targets – 4N (99.99%) and 4N5 (99.995%)
- Nickel Chrome (NiCr)
Technical & Quality Considerations
RSC employs processes designed to achieve a homogeneous grain structure to optimize sputter rate uniformity deposited on the substrate. Processes also minimize incorporation of oxygen into the target. We use proprietary quality controls to characterize and lock-in specific processes for specific part numbers. The same quality controls can be used to certify product is free from voids, inclusions, and meets purity requirements.
Applications for Sputtering Targets
Large Area Coatings (LAC)
The primary market for LAC is architectural glass coatings. Low emissivity, or Low-E coatings on window glass serve to reduce energy costs by reflecting infrared wavelengths outward in hotter weather to prevent indoor heat gain. In colder weather, the coated glass is designed to reflect heat inwards to prevent heat transmission, and thus heat loss to the outdoors. The same glass coating layer stacks are designed to optimize transmission of visible light, reduce glare, and minimize UV wavelength transmission to the indoors. Modern window glass can have more than 15 sputtered thin film coating layers.
Medical Devices and Products
Precious metals have unique qualities useful for the medical industry. Silver targets are commonly used to deposit antimicrobial coatings. Other precious metals such as gold, platinum, and palladium often find uses for their electrical and chemical stability in medical devices and sensors. One example is glucose monitoring strips for diabetes control and management.
Electronics and Semiconductors
High purity gold (Au), silver (Ag), platinum (Pt), and palladium (Pt) sputtering targets.
Precision Optical Coatings
Gold and silver sputtering targets are commonly used for depositing demanding laser coatings for beam splitters and specialty mirrors.
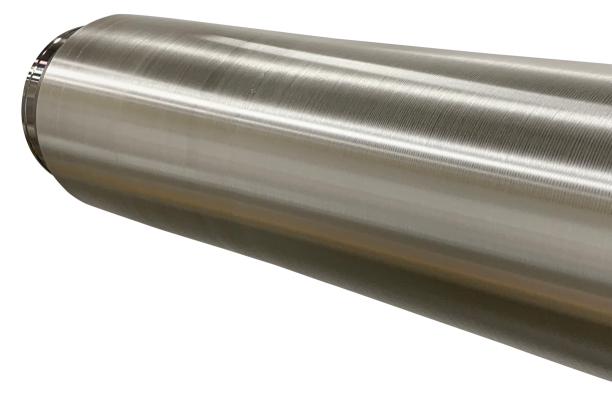
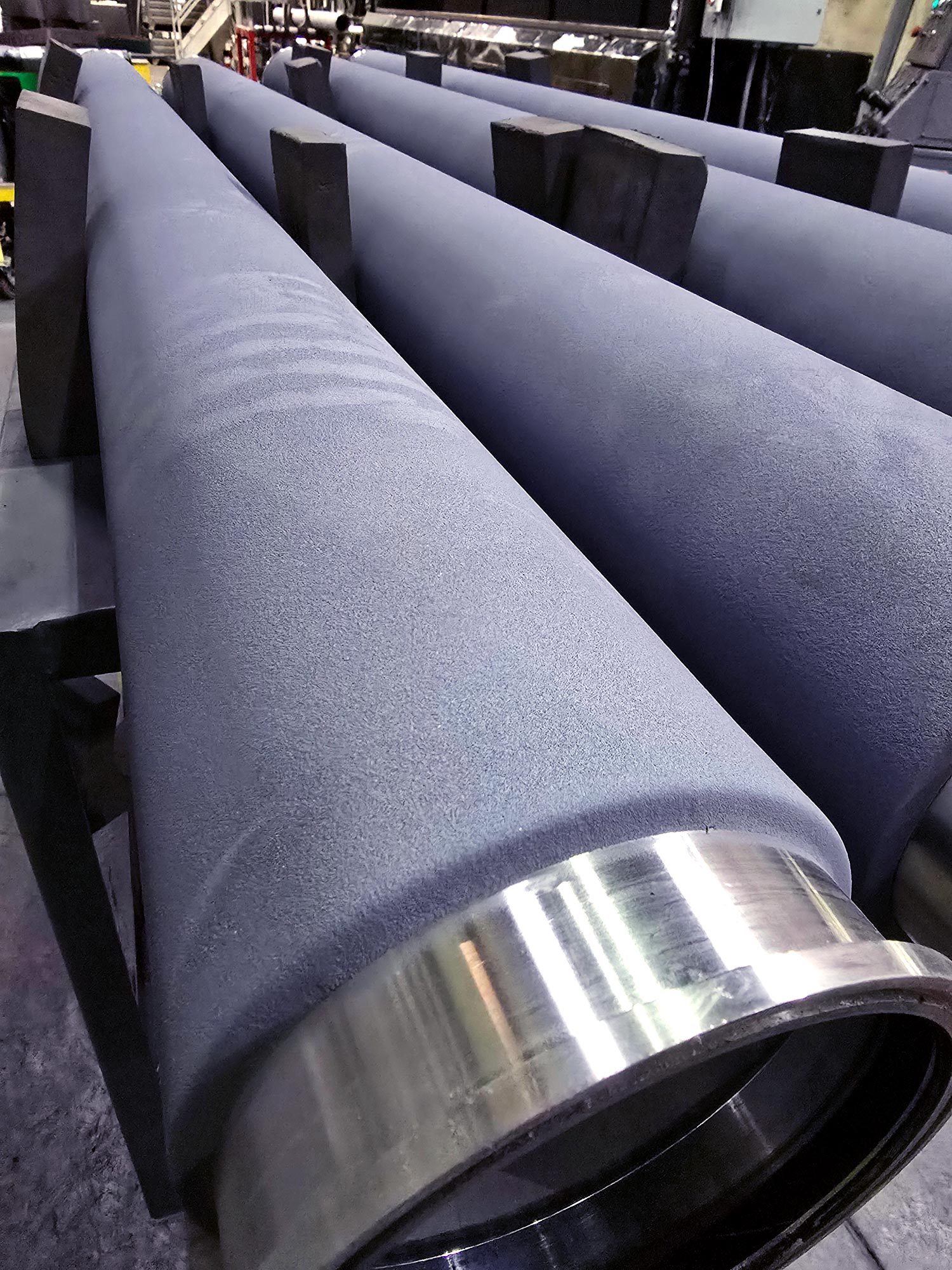
Rotatable Sputtering Targets
99.99% (4N) Minimum Purity Silver
Questions about your application?
If you have any questions about the suitability of your application, please contact us. As well, we can discuss the economic considerations or tradeoffs of planar versus rotatable silver targets.
Technical Capabilities
We specialize in rotatable targets ranging in length from 500 mm to 3,897 mm (approximately 20 inches to 153 inches). Target thicknesses of up to 15 mm are also within our capabilities. However, it is important to consider the total weight of the target during equipment design and process planning, as longer silver rotatable targets can become quite heavy.
- In architectural glass coaters using targets that are 3,191 mm or longer, very thick silver coatings can sometimes lead to slight sagging in the middle of the target due to weight. This can affect coating uniformity. Fortunately, this issue is generally not a concern for shorter targets under 2 meters in length.
Our thermal spray process has been specifically selected and optimized to maintain low oxygen content in the coatings. After evaluating a range of manufacturing methods—including thermal spray, cold spray, casting, and other rotatable target production techniques—we chose this process for its optimal balance of cost-efficiency and desirable technical properties.
Available Targets
- Ag
- Au
- In
- InSn
- Ni
- NiCr
- NiW
- Si
- SiAl
- NiCr
- Nb
- Sn
- TiOx
- TiZrOx
- Ta
- ZnSn
- W
Applications
Applications include web coaters and large area glass coaters, where our silver rotary targets have been successfully used in low-E glass coating stacks, window films, anti-bacterial coatings, and high temperature superconductors.
Additional Considerations
Reclaim of residual coatings is also a part of the complete cost of ownership. In some instances, it’s also economical to re-use the backing tubes. Silver alloys with gold, indium, tin, copper and other elements are possible.
Evaporation Materials
Questions about your application?
If you have any questions about the suitability of your application, please contact us.
What is Evaporation for Thin Film Coatings?
Evaporation is a form of physical vapor deposition (PVD) where material is heated to a high vapor pressure, often in molten state. The vapors are then condensed on to a substrate to form a desired thickness of a thin film. In our case, a thin film precious metal coating. The heating is typically accomplished via resistive heating or by E-beam (electron beam).
Why Use Materials Engineered Specifically for Evaporation?
Engineered pellets or slugs are manufactured with specific form factors intended to vaporize at known rates. Often during evaporation processes, “spitting” results in liquid droplet material splattering on to the substrate. Engineered pellets are made with specified metal purities and processes intended to minimize incorporated gases and impurities to mitigate “spitting” in process.
Technical Notes / Parameters
A quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) is widely used to monitor deposition thickness during process. A QCM is based on a reverse piezoelectric effect such that a mechanical strain or deflection occurs when an electric field (voltage) is applied to the quartz. In the case of a QCM, the electric field is alternating in voltage, thus causing the crystal to vibrate at its resonant frequency inherent to quartz. As a thin film coating builds on the quartz crystal, its mass changes. This results in a change in the vibration or frequency of oscillation.
Two additional factors come into place in order to correct the QCM. The QCM is designed to be in the chamber aside from the substrate, otherwise one or the other would shadow the deposition of the other.
- The tooling factor is a situation or design specific factor which is a consequence of the chamber design and specifically the placement of the sensor and substrate in relation to each other. The tooling factor is a calibration of deposition rate on the sensor compared to what is actually occurring on the substrate.
- The Z-factor, also known as z-ratio, is inherent to the material being evaporated. The Z-factor is essentially a correction factor to account for the fact that the resonant frequency and density of a particular material deposited on the quartz crystal is not the same as quartz, but rather at some ratio to quartz.
Target Bonding
Bonding Planar Targets to Backing Plates: Ask Us About Material Options Available
Questions about your application?
Choosing the bonding technique depends on your materials, operating temperature, and whether you need reusability or special handling of fragile targets.
What is Target Bonding?
Target bonding involves securely attaching (bonding) a sputtering target to a backing plate to ensure stability, optimal heat transfer, and good electrical contact. Without proper bonding, the target may crack, warp, or delaminate resulting in poor film quality, process interruption, substrate and equipment damage. RSC employs ultrasonic scanning of the bond-line to ensure the integrity and quality of the bonding layer.
Why Proper Target Bonding is Important for Deposition Materials
- Enhanced Heat Dissipation: A bonded target enables good heat transfer to the cooled backing plate, preventing overheating, and allowing higher sputtering power and faster deposition rates.
- Mechanical Stability: Choice of backing plate and type of bonding can accommodate and minimize thermal expansion mismatches between the backing plate and target material. There can also be substantial cooling water pressure on the backside of the backing plate. A rigid backing plate of sufficient thickness can allow good thermal contact to the backside cooling while be rigid enough to avoid warping.
- Economics: Especially with precious metals, for cost and working capital reasons it is often desirable to have a thin target material. An appropriate backing plate becomes the rigid base for the thin target material.
- Common Approach: C10100 grade of copper (Cu) is commonly used for a backing plate material, especially for precious metals. This alloy code designates high purity Cu >99.99% pure. It is often known as OFE (oxygen free electronic) Cu or otherwise known as OFHC Cu (oxygen free high conductivity). The bonding agent is typically an indium based material.
- Other backing plate materials, Cu alloys, or different bonding agents can be considered for particular challenges. Please call and speak with an engineer to discuss specific circumstances.

Let’s build something reliable together.
From consultation to delivery, RSC is here to help you every step of the way.
"*" indicates required fields